This week’s podcast is about Elon Musk’s take-over and turn-around of Twitter. Lots of cool lessons in what he has done in the first 3 weeks.
You can listen to this podcast here, which has the slides and graphics mentioned. Also available at iTunes and Google Podcasts.
Here is the link to the Asia Tech Tour.
Here is the “audience-builder platform with connected users” I mentioned: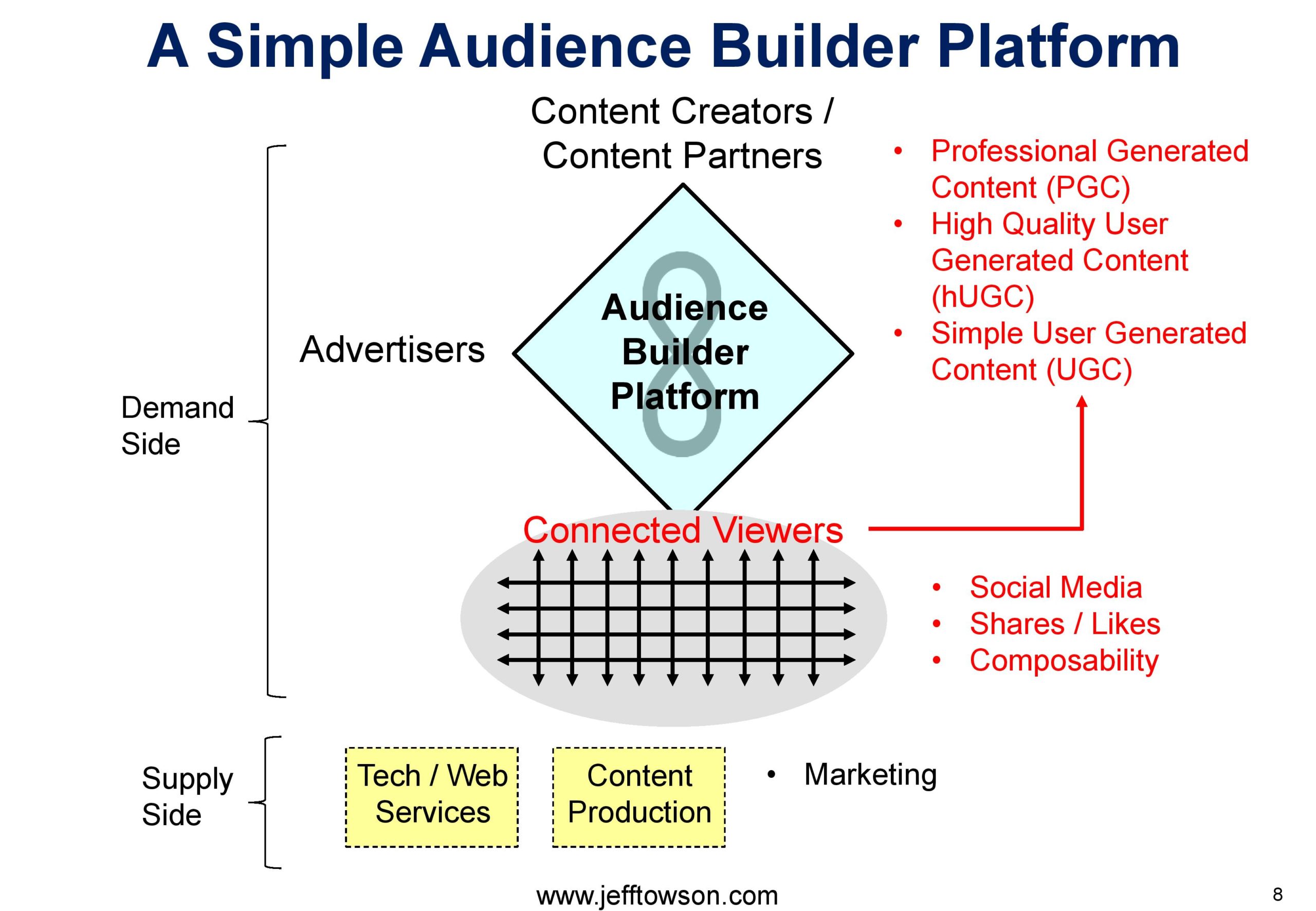
Here are the 6 levels and digital operating basics:
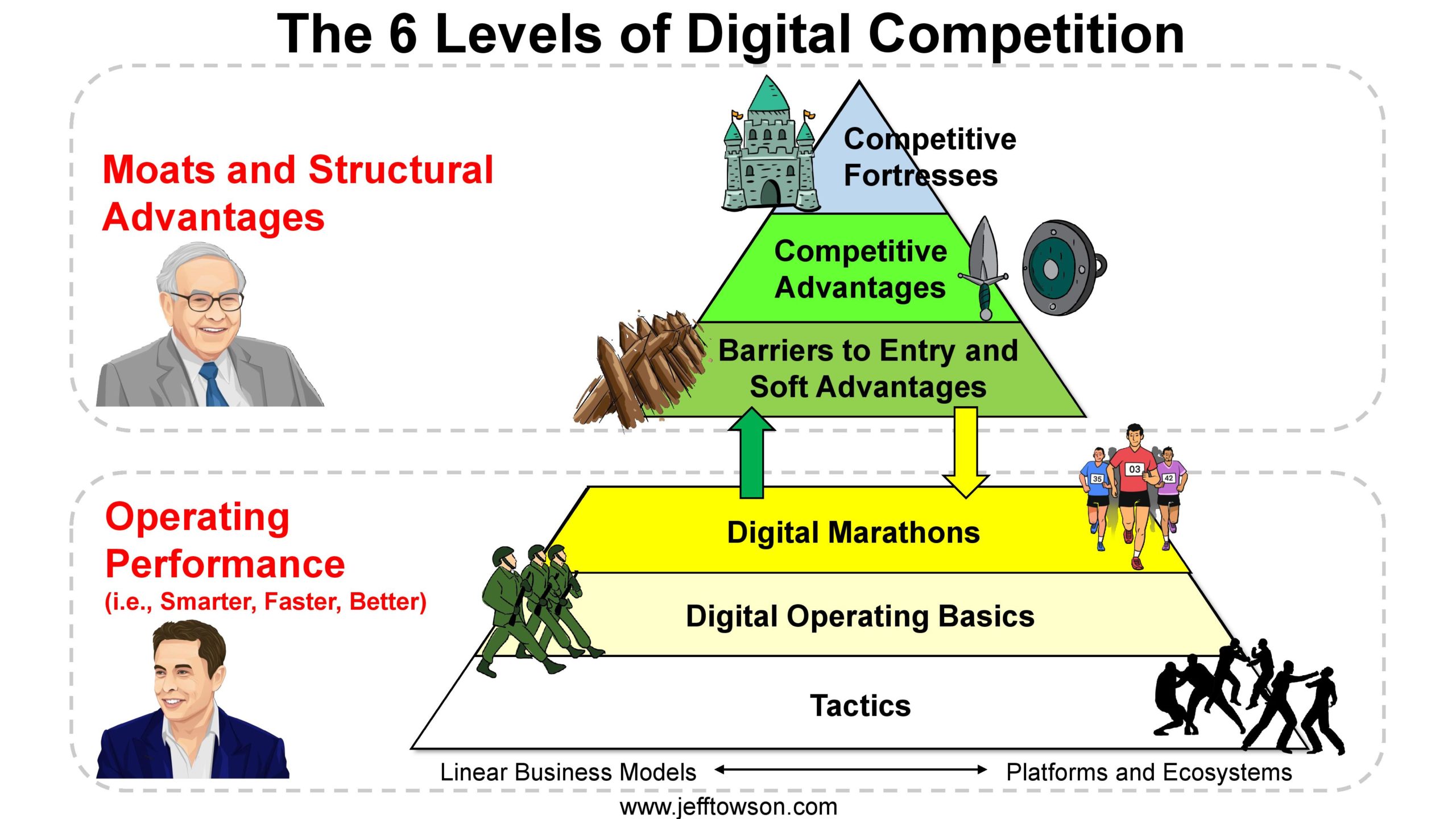
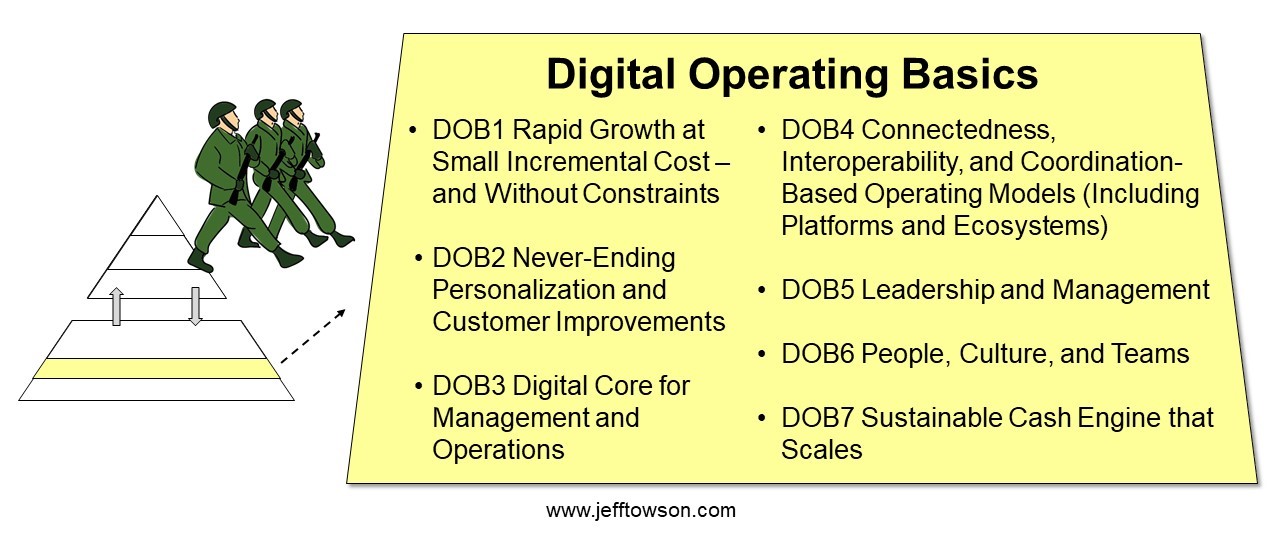
——
From the Concept Library, concepts for this article are:
- Audience-Builder Platform with Connected Users
- Digital Operating Basics
- Social media
From the Company Library, companies for this article are:
Photo by Brett Jordan on Unsplash
———-
I write, speak and consult about digital strategy and transformation.
My book Moats and Marathons details how to measure competitive advantage in digital businesses.
I also host Tech Strategy, a podcast and subscription newsletter on the strategies of the best digital companies in the US, China and Asia.
This content (articles, podcasts, website info) is not investment, legal or tax advice. The information and opinions from me and any guests may be incorrect. The numbers and information may be wrong. The views expressed may no longer be relevant or accurate. This is not investment advice. Investing is risky. Do your own research.
Episode 145 – Transcript from Otter.ai
All content included
The topic for today, Elon Musk’s strategy for Twitter, which is supercharged performance and to fix the product.
Now, as always, there’s a couple of sort of digital concepts today, it’s not going to be anything terribly new, maybe one bit that’s new. But this will just be the digital operating basics, which I’ve talked about forever. A little bit about digital marathons, which I’ve also talked about further the smile marathon and then payment platforms. Maybe the one bit which is new, which I haven’t really talked about is within Audience Builders, Audience Builders, a platform type, where you’re you have two user groups, you’re in the interactions business, and you’re facilitating and enabling interactions, in this case, between people who create content creators and people who consume content. So that’s YouTube that’s Tik Tok to user groups. Very nice network effects tends to have a lot of long tail content, which makes the network effect particularly powerful. But there’s sort of a subtlety in this and I’ll put a slide in the show notes, which is on the web page, unfortunately, can’t put them under iTunes, which is this idea of if the interaction is between a content creator, let’s say someone who’s making a short video on tick tock, and someone who’s watching videos, like everybody. Those can sometimes be the same people. But I put them as different user groups because they’re, they’re doing different roles. So it doesn’t necessarily mean they’re different. Someone who watches videos can turn the phone around and become the content creator as opposed to the content consumer. Okay. And that’s very easy to see in something like YouTube, because most people don’t make YouTube videos. When you get to tick tock. It blurs a bit more because it’s pretty easy to go back and forth. Well, when you move on to something like Twitter, it’s really seamless, like, Okay, I’m reading tweets, and now a tweet went out. Did I just to become a content creator. So as you move more into sort of these discussion platforms, the whole idea of a two sided platform, I think it kind of breaks down a little bit. This distinction, this model I’m using, it’s a very good model for something like YouTube, it’s a very good model for people leaving reviews on TripAdvisor or Expedia. At a certain point, when it’s just sort of a long running back and forth conversation in a Reddit or a Twitter. This model doesn’t work that well. It’s sort of like, yeah, isn’t everyone just talking is this really a two sided platform with two user groups, and we’re getting network effects. Because we’ve standardized the interaction, it’s like not really. So when you look at something like Twitter, and when you look at something like Facebook, the distinction between content creator and consumer is so vague that I generally don’t talk about them that way. You know, all of these frameworks, I’ve given, you know, 50 different concepts on the concept library. They all work in certain places, and they start to not work in others. And you got to kind of know when this framework isn’t helping you anymore. So Twitter, Facebook, social media, I don’t usually talk about them as two sided platforms, Audience Builders, I think there’s something a little bit different, and I don’t quite have a great name for it. So that’s sort of one distinction to think about. The other distinction to think about is, if I’m on a marketplace platform, Lazada, Taobao shopee. I can be a consumer or I can be a merchant to user groups, I go on as the consumer, I buy my goods. That’s pretty much the end of the interaction, I’m not going to share my goods, oh, look what I just bought on Lazada. Even though if you’re on Lazada, they always trying to get you to share what you just bought, you know, you just booked a trip, share it with your friends, they’re always getting you to sort of share on social media for marketing purposes. That’s kind of one where that doesn’t happen on marketplaces. But it happens all the time on something like Twitter, something like YouTube, because people tend to share content like crazy. You know, they share videos, they share Instagram photos. So the way I sort of described this, I’m going to put the graphic in the show notes. I describe it as an audience builder platform. But the primary user group is not consumers, it’s connected consumers. Which means maybe a consumer on tick tock watching videos is a connected consumer, and they will share the video with their friends. That’s kind of how I make that look. And that’s kind of how I consider Facebook and Twitter. And these is they’re sort of just networks of connected consumers. And then platforms feed into that. And I’ll show you the graphic. So it’s a little bit of a distinction. But it also I think, makes it much easier to understand. And we don’t see any of that on the other platforms very much people don’t share what they bought on a payment platform. They don’t share what they bought on Lazada. You know, but it really does happen on Audience Builders, there’s a lot of sharing between the consumers. So anyways, take a look at the graphic. I think that’s a pretty important distinction. But I’ve never really had a great way to describe something like WhatsApp, or Facebook, in any of my five platform types, it doesn’t really fit that well, in those. You know, it’s the way I think about it is Andreessen Horowitz uses this, which is anytime you can take a product or service and add a social layer to it. They call it social plus, it makes it more robust. So that’s kind of how I view that it’s like, we have a basic audience builder, and we’ve added a social plus layer. But it’s not really a platform in its own right. Anyways, that’s a bit of theory, take a look at it, see what you think. If you have any suggestions, let me know. Alright, with that, let me get to the content. So those sort of the concepts for today digital operating basics, smile marathons, and then we’ll call it audience builder with connected users, audience builder with connected viewers, something like that.
Elon Musk is absolutely rocking and rolling at Twitter, like the speed at which he’s moving is stunning. I mean, Twitter has been a screw up for 10 years, like, it’s the way I’ve always thought about Twitter is like, if you look at the share price of Twitter, before all this happen this year, and 10 years ago, it’s about the same. Like what social media is one of the few social media companies in this world. And you had the largest tech Bull Run we’ve ever seen, and you didn’t move your share price in a decade. Look at look at Facebook 10 years ago. So it has just been a basket case of a company. And I think it’s two things.
There’s my little diagnosis, I think the product has always been half broken. I think part of the part of the product is definitely engaging people like the product people are on there all the time, you can’t ignore the fact, people spend a huge amount of time on Twitter. However, people also leave, like the number of people that have used Twitter and left is like 90%. So there’s something about this product that’s compelling. And there’s something about this product that’s broken. And even today, you’ve only got 200 million users, like, you know, Facebook and YouTube and even tick tock, they’re up at 2 billion now. So you’ve got a good product, but it’s fundamentally broken. And then on top of that, you have a very ineffective management team that can’t get anything done. They haven’t made even they haven’t been able to add an edit button. You know, it takes a years. And then you’ve got this bloated, lazy culture, where, you know, it’s basically looks like an adult daycare center. Elon Musk has been tweeting in the last couple of days, about his taking away free lunches, because they get free lunches. And he said this was costing like $400 per person per lunch. And someone who worked at Twitter, because he’s fired half of them, tweeted in and said, That’s not true. I was in charge of this program, it’s 20 to $40, per lunch, he tweets back, and he says, No, the average cost works out to be 400. Because the percentage of employees that were actually in the office on a daily basis is under 10%. So you have an empty shell, and they didn’t even offer the meals at dinner, because there was nobody there. I mean, what kind of company has under 10% of their staff coming in, even with the COVID thing, the free meals, they have a meditation room, they have a free wine bar, they more or less doubled their staffing in the last five years and has anything improved. And ultimately, this is just a software company. When WhatsApp got bought by Facebook, for $19 billion, they had 50 employees. Facebook had, I mean, Twitter had 7500, up from three or 4000, you know, five years before something like so this is just a bloated company. Lazy daycare, it looks like a lot of but the bad stuff that happens at US colleges now where it’s just the soft, in my opinion, people who don’t work that hard, who all get these crazy sell. And it’s that’s how it looks to me. So then you get you get this guy flying in. So here’s the pace, like the dates are really important. So he takes it over on October 27. So about three weeks ago, you know, he did the thing where he shows up in the lobby carrying a sink with the joke, let this sink in. It’s like a total dad joke. It’s not really a good, just so dorky. He goes upstairs, it’s on a Friday. He immediately fires the CEO and the senior management and one of them got escorted out of the building by security. He immediately deploys his people from Tesla and SpaceX, so he doesn’t show up alone. He shows up with the team. And this is the team that can land rockets, which nobody could ever do before. This is you know, these are hardcore engineers. You know, these are not people who have wine bars, and beanbags and meditation rooms to relax. And so that’s kind of thing now that was just one week with that was day one. Within the first seven days, he fires half the employees within seven days. One week after that, he launches the new verification button. So he mean he mandated a new feature, you can sign up and get your blue checkmark. They execute and deploy 10 days. Twitter’s never done anything in 10 days. And as I’m doing this podcast, it’s on a Tuesday. He’s sleeping in the Twitter headquarters. There’s pictures of him. He’s living in the Twitter headquarters right now. And he’s telling people like if you have ideas, come and talk to me anytime I’m here. Like that is such a tremendous culture shock. That’s why supercharging performance. I mean, this is really shock therapy. Right? This is like where you take your average lazy, Stoner high school student you’ve had enough of is your kid and you put him in the Marines one day, and Monday morning. He’s getting up at 4am running for five miles with a shaved head. I mean, it’s this level of just like shock therapy. So it’s app salutely fantastic to watch. Okay, so that’s kind of what’s going on. Let me break it down. So I’m gonna give you, let’s call it two points, point number one supercharge operating performance point number 210 x the product, which basically means like, the first thing you do is you have to change this company from top to bottom, just get it running better. Once you get that done, then you try and launch a dramatically improved product or service, such that the value of the company is dramatically better. Right, so a 10x product a 10x service. Now, I think we can actually see his playbook for both of these. Okay, so if you look at my standard graphic, which I’ll put in the show notes of my six levels of digital competition, it basically, you know, my sort of analogy has been, you have to win it two levels, two levels as a digital business, you have to win on operating performance, and you have to win at moats and structural advantages. And the symbols I’ve been using is Elon Musk and Warren Buffett. Elon Musk is arguably arguably the hardest charging operator on the planet. I mean, nobody works like this guy. Well, I mean, I’m sure there are, let’s call him, the most famous of them, maybe Bezos and some others that are at this level. But there’s a very small group of people who can operate at this level. He’s one of them, and then buffets, more of the Hey, it’s not about working hard. It’s about building a structure that nobody can compete with. So those were my two levels. So if we look at what he’s doing, we’ll call that Twitter. 1.0, his first version, he is just supercharging, the operating performance of this business. And I gave you seven digital operating basics. I’ll put the slide in the show notes. He’s going through 12345, he looks like he’s going through five of them. If you look at my list, I’ll read them to you. It looks like he’s doing five of them. That’s most everything I see him doing is these five things. So number one, let’s call it DOB five leadership and management. Okay, he fired them on day one. He’s in charge. And he brought in his, you know, gung ho team. From I think it’s Tesla. I’m not sure it’s probably more test it on Tesla or SpaceX. So digital operating basics five, leadership and management, bam, day one. Okay, digital operating basics, number six people culture in teams. I think that’s why he’s been doing this shocking stuff in this first week. I think that’s why he’s fired. I think that’s why he’s firing 3500 People in the first week, part of it’s because it needs to be done. Part of it is because he shocking the culture. Right? He is letting everybody know, you know, if you want to work like a crazy person, you’re welcome to stay. If you don’t want to work like a crazy person, I get it, you’re welcome to leave, like, he’s going to fire a lot of people, but a lot of people are going to leave on their own. Because they don’t want to be part of this maniacal culture. And that’s why he’s doing things like no more working from home, forget it. And his language on this is like, they had an all hands meeting. And here’s a quote, let me be crystal clear. If people do not return to the office, when they’re able to return to the office, they cannot remain at the company, end of story. That’s it. If you can show up in an office, and you do not show up in an office, resignation accepted End of story, unquote. I mean, this is just now he talks. So let’s call that, you know, that’s a bit of a shock. But his other quotes are more about, you need to have a maniacal sense of urgency. And that’s his phrase. So here’s a quote, let’s take action. I’m a big believer in having just a maniacal sense of urgency. So if you can do it after this meeting, I would do it after this meeting, just a maniacal sense of urgency. Like if you want to get stuff done, just go hardcore. Right? So he’s sort of doing this idea of changing the culture below the management level, changing the staff and the way I’ve heard it talked about, which I think is probably true. He’s basically reconstituting the entire staff of Twitter. And he’s pulling from two places he’s pulling from the current staff. And then he’s pulling from Tesla and SpaceX, but the Twitter that existed two weeks ago is gone. You know, you’ve got to jump to the new Twitter, but he’s not just bringing those people in. Now most companies I’ve done some turnaround where I’ve fired you know, hundreds of people. The problem when you come into a company like this is if you fire a bunch of people, things start to break, which is true. And then you have to hire people which takes time. So you tend to be hesitant And not that aggressive.
He doesn’t have to do that because he can fire like crazy. And if stuff breaks, he’s got two other tech companies in his back pocket he can pull people from, you know, most people, if they fire aggressively, then they have to start up the hiring process and find new people. And sometimes the new people are worse than the current people. He doesn’t have that problem. He’s got 10s of 1000s of people in his back pocket he can pull from, so he can be a lot more aggressive. Okay, so that’s dob, six people, culturing teams, dob, two digit digital operating basics to never ending personalization and customer improvements. I mean, this is where you just start. And he’s been doing this in, like in the open on Twitter, where he is just floating idea after idea. And he’s been telling his staff, you can sit in the meetings, if you have any idea. Just send it to me. We want new ideas. We want new ideas, anything. And he changed his bio, his title on his Twitter account, to like, chief complaint officer. And he basically went on and said, the chief complaint officer for Twitter’s now online, please submit your complaints. And people just started putting hundreds of comments. So he’s looking for this, he’s beginning the process of never ending very rapid customer improvements. Just make the product better every day, every day, not over six months, every week. And this is what the best software companies do. Especially gaming companies are really good at this, where they will release new edits to their game and new features and new improvements every single week. They work at this crazy pace. So that’s what he’s doing. He’s hunting for stuff. And he already pulled the trigger on one, he said, we’re going to do blue checkmarks for everybody, that’ll probably solve the bot problem. He announced it 10 days later, it went live. I signed up, it worked beautifully. Right. I mean, Twitter has never moved this fast. But it’s also this process of you know, and here’s another quote from him, quote, I very rapidly want to improve every aspect of Twitter. That’s digital operating basics. Number two, it never, and this won’t end, it will just keep happening for years, that every week, every two weeks, they just keep making little things better and better and better. And the best digital companies that this is how they behave. Okay. Last two, digital operating basics number one rapid growth at small incremental cost. Now, this is where you start to get to the idea that like, why isn’t Twitter 2 billion people? I mean, why not? It’s been around for a decade. Like why is it the only social I mean, WhatsApp has it WeChat has it they all have it, Instagram has it. You know, even Pinter, I mean, why is it so small? If you’re going to be a software company, one of the biggest benefits of being a software company is you can get global scale without a global cost structure. So if you’re a pure software company, and you’re not global, what’s the point? I mean, open supermarkets or something. So he’s spoken to this a lot that, you know, daily active users Twitter’s about Twitter billion. He wants it to be a global platform. Here’s his quote, there are 8 billion humans if we don’t have at least a billion humans on the system, then we have a very small percentage of humans. So we want a reasonable percentage. He says, quote, YouTube has 2.6 billion users. Oh, man, we’re nothing. So he’s clearly going for scale. So this would all be under Twitter 1.0. Well, we’re going to improve things. We’re going to supercharge the management, the culture, and we’re going to go for scale with a moderately improved version of what we have. That to me is Twitter one point out. The last bit, he’s talking about his cashflow, he’s been talking about cashflow an enormous amount. And it’s probably because he borrowed a lot of money to do the acquisition and he paid you know, way too much for it. Now, people criticize him on line for this as Oh, you levered up, this thing’s gonna go bankrupt. You know, who really performs his company’s private equity people who load up companies with debt. You know, the old saying is like, uh, you know, if you load up a company with debt, it’s like driving a truck and someone is has put a knife coming out of the steering wheel. You are really paying incredible attention. You know, debt is a sword equity is a pillow. So the fact that he’s borrowed money, I think that’s just going to make him more maniacal. So he’s been talking a lot about cashflow. One because I think of the debt too because there’s this idea of recession in the next year, and all the tech companies are firing people right now. Right? Everybody’s scaling back and getting ready for this. So he’s had some pretty stark words for this. He says, quote, We just definitely need to bring in more cash than we spend. If we don’t do that there’s a massive negative cashflow, then bankruptcy is not out of the question. That is a priority. We can’t scale to 1 billion users and take massive losses along the way. Right. And digital operating basic seven is basically called you’ve got to have a sustainable cash engine that scales. I mean, I put those words in specifically, it’s not about just having a cash engine that can pay for itself, you want it to get bigger as you get bigger. And he talked a lot about the recession, quote, I’ve been through the recession of 2000 2001 2008 2009. There’s not and I’m somewhat paranoid about dying in recessions, I have recession, PTSD from keeping x and Pay Pal alive through the 2000 recession, keeping Tesla alive in the 2009. Recession. It’s worth remembering in 2009, General Motors and Chrysler both went bankrupt. Tesla did not despite being a startup Electric Vehicle Company. So he’s definitely focused on this. He says, I don’t know what the revenue shortfall will be next year. But I think it’s possible that we could see a net negative cash flow of several billion dollars. So he’s focused on cash flow. Anyways, that to me is Twitter 1.0. And I think the digital operating basics and you know, the short version of that is, we’re going to supercharge operating performance. And if anyone can do it, this guy can do it. So that looks pretty great. And I think that’s most of what’s been in the news for the past three weeks.
With that, let me move on to the next point, which is 10x the product? So Twitter 2.0. Or we could call it 2.0 and 3.0. How do you make this company worth dramatically more than it is today? Well, you have to change the product. The product is what it is. Everyone knows what Twitter is, if it gets bigger, that’s going to make it more valuable. If he gets to a billion users, that’s great. But how do we make the product fundamentally more valuable? Well, he’s pretty much tipped his hand on what the first steps are going to be. And it looks like it’s going to be a payment platform, and an audience builder platform, you know, to have the type we’ve talked about. So here’s what he said in a town hall meeting last week, quote, I think there’s a lot that is very, very obvious that we need to do like video content and compensating creators in order to get content on Twitter. That’s a no brainer, high priority, improving search high priority. Well, you’re obviously going to add payment capability to Twitter. That’s a high priority. So he’s he’s mentioned at least three things as a high priority payment, content creators and search, but search, he’s not talking about a search engine. He’s talking about search within Twitter as it exists now. So that we’ll call that a function, but not not a major strategic move. Okay. Twitter is like, I mean, it is an audience builder platform in the sense that people there, it’s not like Facebook, where everyone is just sharing text back and forth. There are certain people who create the vast majority of the content on Twitter, highly followed people, there’s a small subset that you could call the content creators. It’s not just back and forth conversation with everybody. So in that sense, you could argue this as an audience builder based on text. Fine, but those people don’t get paid. They don’t get any of the ad revenue. And most of those people are posting videos and articles. Not just hey, I have a funny comment. Okay, but if you post a video an article, they’re posting it from YouTube and Tik Tok, and then you post it, the person clicks on it, and it takes you over to Tik Tok or YouTube. So by not giving content creators, the ability to one get paid for posting on Twitter and also giving them more types of content they can do not just text. And it’s pretty clear. He wants to go for short video. So if you’re a content creator on Twitter, you can post tweets, and you can post short videos. And that’s kind of a no brainer. So we can call this sort of strategy him building an audience builder. With connected users, we can call that a copy of tick tock. And that’s what he’s been talking about is a copy of tick tock basically.
What does that get you? You basically Win Win Win, number one, it creates a new business model that is inherently very valuable. YouTube is a tremendously valuable company. So This makes Twitter the current Twitter plus a small version of Tik Tok, or a version of quiet show. And this is exactly what WeChat did WeChat some messenger. But very quickly, Alan Jiang said the future of WeChat has to be short video, and he created a short video function within WeChat. Because it turns out, it’s super valuable. But it also gets you more engagement, it gets you more users, people don’t spend two hours on Twitter. But people spend 90 minutes watching videos on Tiktok. So he wants to get more users. He wants to get more screen time. And to do that, he’s going to add the single most popular type of content right now, which is short video. And the content creators are going to get paid. I mean, it’s just an audience builder. So you could call this, he’s going to copy he’s going to build a tic tock within Twitter. And they already had a company years ago called the vine, which is where you used to share gifs like short little memes. Vine could have been Tik Tok. And here’s a funny thing. Vine is about sharing gifts. The main competitor to Tik Tok in China is quite show, qui show was vine. It was a platform for sharing gifts. And then when they saw what was happening, they pivoted into short video, Vine could have done the same thing. So he’s already said something like, here’s some quotes from him. We also want to expand to be sort of a multimedia platform. We are that to some degree, we are the strongest when it comes to anything that’s writing in real time. But we also want to have that for pictures and video video and not in a way that copies what others do. Quote, do we have a compelling short form video as opposed to exactly what what vine was? It’s not let’s copy vine from whatever year with ancient code. It’s really about how do we have compelling short form video, just compelling content in general. Okay, and then he says, you know, right now, content creators cannot post the length of video that they would like to post, then they cannot monetize it, which means they cannot pay their bills. These are not like super complicated things. They’re pretty basic. We’re not trying to put you to about a business, but I’m just saying Do we really need to give YouTube a whole bunch of free traffic. So let’s give creators the option if they would like to put their video on Twitter and earn the same amount as they would or maybe slightly more on YouTube or Tik Tok, or whatever the case may be. So those are his comments. So he’s clearly going after that makes all the sense in the world. So that’s another business model. Next one final one payment platform. He’s been talking, this is one, the one he’s actually talking the most detail about, because this is the guy that founded PayPal. So he really does understand payment. And he said they had some sort of super business plan, they wrote back in 2000, that was going to be the ultimate payment financial services app. And then they built part of it for Pay Pal. But he actually talks about I wrote this business plan in 2000. We never executed most of it. So he’s got really detailed comments on what he’s going to do with payment. And he basically says, here’s a quote, I think that I think there’s this transformation, transformative opportunity in payments. And payments really are just the exchange of information. From an information standpoint, not a huge difference between say, just sending a direct message and sending a payment. They’re basically the same thing. So basically, you can send money to people, which is pretty much what WeChat did, they were a messenger and wechat used to say the exact same thing. We can send payments as easily as we can send messages on WeChat. Okay, so let’s say he’s going to build a payment platform. Now that can be a very valuable business. But if you look at what ant financial did, and new bank did in Brazil, they used payment to leapfrog themselves into a financial services Super App. Once you get payment, you can start to add things like checking accounts, money, market accounts, credit, and then maybe depending how ambitious you are, you can go into wealth management, you can go into insurance and other things, which is what new bank is doing in Brazil, what’s ant financial did here. And literally, that’s what he’s talking about. So he said, here’s a quote then in order to get money out of the system in parallel, we establish a high yield money market account, so that having a Twitter balance is the highest yield thing you can do. So that’s let’s add a money market account. As long as you’ve got a digital wallet, that’s exactly what Alibaba did with you about. That’s how they created the world’s largest money market account was they said, look, you’ve already got money on Alipay. Instead of letting it sit there in your wallet, why don’t you put it in our money market account? Here’s more Elon quote then To attach a debit card to the Twitter account so that you have backwards capability into the payment system, because not everyone will accept Twitter, then if you have, so basically he’s going from payment to money market account to debit card, so you can go backwards and forwards compatibility. And then in theory, he could go into credit financial services, more wealth management products, which is just what these other companies are doing. So second big 10x opportunity payments, into money markets account and maybe into a financial services Super App. Wouldn’t surprise me if he’s going to be very aggressive there. That’s kind of what he’s talked about one last point, and then I’ll finish up here. The thing he hasn’t talked about, which I think he will, so this is a little bit of a prediction. He’s obviously talking about WeChat, a lot that we should copy WeChat. The two things that WeChat has done that he hasn’t talked about. Number one is adding many programs, that once you get people in an ecosystem, and you have payment capability, it’s very easy to start selling them things by offering all the merchants and brands, abilities to put their shops on the platform, which is exactly what tic tock is doing. It’s what YouTube is doing. It’s what Facebook is doing. So he’s well positioned to move right into E commerce. And that’s huge money. I mean, that’s that’s a massive opportunity. And from there, in theory, he could go into search, which is what WeChat is doing right now, because they have all the mini programs, you can search the content of all the mini programs, hundreds of 1000s of them. So you can do one search engine that searches everything on your smartphone more or less. So that would be the two other big sort of ideas on the horizon. So there’s at least four ideas there to 10x the product. And that’s about where I am in sort of my thinking on this. One last comment. I always talk about digital operating basics, digital marathons and then structural advantages Moats. What is the digital marathon that he’s going to be running here, that such that as years go by, he pulls so far ahead, nobody can catch him. Now when he does Tesla and SpaceX, the digital marathon he’s running is sustained innovation. That’s the essence smile, smi le smile marathon, the actually it’s not the SDI stands for sustained innovation. His rockets keep getting better and better and better at such that nobody can build the rockets that does what he does. Now, I don’t think that’s what he’s building at Twitter, I don’t think Twitter is a bunch of groundbreaking engineers who are going to figure out stuff nobody can do. It’s a software business and a platform business model. We are not inventing new types of ways of going to Mars. So I think the digital marathon, he’s going to run his ecosystem orchestration, which is the E in smile, and hyperscale and hyper growth, he’s going to basically do what Tik Tok did, which is we are going to innovate, we’re going to be a very good ecosystem orchestrator. And we’re going to get very, very big. That’s the marathon and when we’re up at 2 billion users will be impossible to catch. Something like that. So I would put it under that category, which is a little different for him.
